FULL VIDEO 👇👇
Botflies are a group of parasitic insects that can infect humans and animals, causing discomfort, pain, and in some cases, secondary infections. The lifecycle of these creatures involves their larvae, commonly referred to as maggots, living under the skin of their host. While botfly infestations are typically more common in tropical and subtropical regions, they can occur anywhere. Understanding how to identify and safely remove botfly maggots is crucial for maintaining health and preventing further complications.
What Are Botflies?
Botflies belong to the family Oestridae, and their larvae are parasitic. Female botflies lay their eggs on a host or a carrier, such as a mosquito or tick. When the carrier bites a warm-blooded animal or human, the eggs hatch due to the warmth of the host’s body. The larvae then burrow into the skin, where they develop over several weeks.
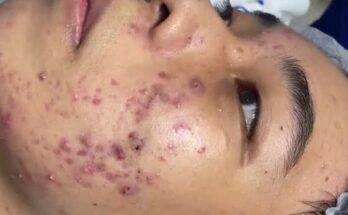
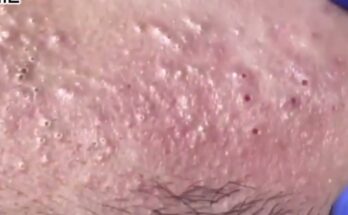
The presence of botfly larvae in the skin is referred to as myiasis. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and a small hole in the skin through which the larva breathes. The area often feels itchy and painful, and in severe cases, secondary bacterial infections can develop.
Signs of Botfly Infestation
Identifying botfly infestation is the first step toward proper treatment. Common signs include:
- Painful Lesions: The site of infestation develops into a raised, painful lump.
- Breathing Hole: A small hole in the center of the lesion allows the larva to breathe.
- Movement Under the Skin: You may feel or observe the larva moving within the lesion.
- Discharge: The wound might produce clear or yellowish fluid.
If you suspect a botfly infestation, it is essential to confirm the diagnosis before attempting removal.
Methods of Botfly Maggot Removal
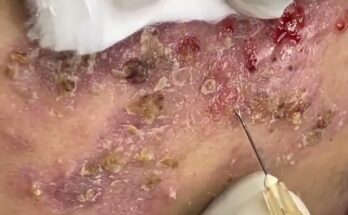
Several methods are available for removing botfly maggots from the skin. It is strongly recommended to seek medical assistance for safe and effective removal. Attempting to remove the larva improperly can result in complications, such as incomplete removal or secondary infections.
- Manual Extraction
Manual extraction is the most common method used by healthcare professionals. The process involves applying local anesthesia to numb the area and using sterile tools, such as tweezers, to gently pull the larva out through the breathing hole. This method ensures the entire larva is removed, reducing the risk of infection. - Suffocation Technique
This method involves covering the breathing hole to force the larva to surface. Substances like petroleum jelly, adhesive tape, or even bacon fat can be applied over the hole. Once the larva surfaces in search of air, it can be carefully extracted. However, this method may require patience and precision. - Surgical Removal
In some cases, especially when the larva is deeply embedded, surgical removal may be necessary. A small incision is made to extract the maggot. This method is generally performed under sterile conditions to prevent infection. - Topical Treatments
In certain situations, medical professionals might use topical agents, such as ivermectin or other antiparasitic medications, to kill the larva, making it easier to remove.
Post-Removal Care
After removing the botfly maggot, proper wound care is essential to ensure healing and prevent infection. Here are some recommended steps:
- Clean the Area: Wash the wound with antiseptic solutions.
- Apply Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent bacterial infections.
- Monitor for Symptoms: Keep an eye on the wound for signs of inflammation, pus, or fever, which could indicate infection.
- Follow-Up: Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider may be necessary, especially for severe cases.
Preventing Botfly Infestation
Prevention is always better than cure. To reduce the risk of botfly infestations:
- Use insect repellent to deter mosquitoes and other carriers.
- Wear protective clothing when traveling to areas where botflies are common.
- Avoid scratching insect bites, as open wounds can attract parasites.
Conclusion
Botfly maggot infestations, while unpleasant, can be effectively managed with proper care and treatment. Prompt recognition of symptoms and seeking professional medical help are crucial steps in ensuring a safe and complete removal process. By taking preventive measures and maintaining awareness, you can minimize the risk of encountering these parasitic pests.