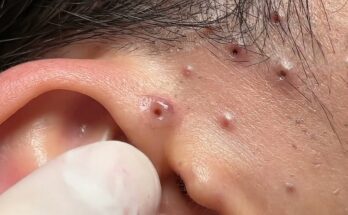
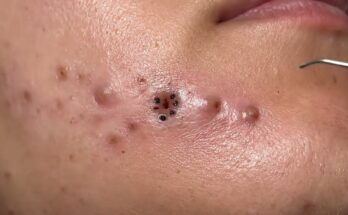
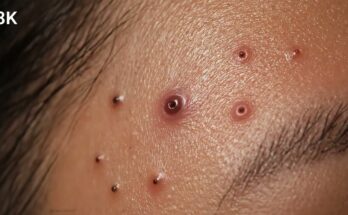
A sebaceous cyst is a benign, fluid-filled sac that forms under the skin. While most sebaceous cysts are harmless, they can become infected, causing pain, redness, and swelling. Infected sebaceous cysts may require medical treatment, including removal, to prevent further complications. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for infected sebaceous cysts, providing clarity on how these conditions are managed.
Causes of Infected Sebaceous Cysts
Sebaceous cysts typically form when the sebaceous glands, responsible for producing oil to lubricate the skin, become blocked. This can occur due to various reasons, including:
- Clogged Hair Follicles: When a hair follicle becomes blocked by oil, dead skin cells, or debris, a sebaceous cyst can form.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical damage to the skin, such as cuts or abrasions, can lead to cyst formation.
- Genetic Factors: Some people are genetically predisposed to developing sebaceous cysts.
- Skin Infections: Bacterial infections in or around a sebaceous cyst can cause it to become infected, leading to increased swelling and pain.
An infected sebaceous cyst occurs when bacteria enter the cyst, usually through a rupture or break in the cyst wall. This leads to an accumulation of pus, making the cyst tender, red, and swollen.
Symptoms of an Infected Sebaceous Cyst
An infected sebaceous cyst presents distinct symptoms, including:
- Pain and Tenderness: As the infection develops, the cyst becomes increasingly painful to the touch, and the surrounding skin may feel tender.
- Redness and Swelling: The area around the cyst may become inflamed, with noticeable redness and swelling.
- Pus or Fluid Drainage: If the cyst ruptures, it may release a thick, yellowish fluid or pus. This is a sign of infection.
- Warmth in the Area: The infected area may feel warm to the touch due to the inflammation.
- Fever: In some cases, if the infection spreads, a mild fever may develop.
Treatment of Infected Sebaceous Cysts
The treatment of an infected sebaceous cyst depends on the severity of the infection and the cyst itself. Options include:
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the cyst may help reduce inflammation and promote drainage. This can provide relief if the cyst is in the early stages of infection.
- Antibiotics: If the infection is mild to moderate, oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
- Drainage: If the cyst is painful and swollen, a healthcare provider may perform a procedure to drain the cyst. This involves making a small incision in the cyst to release the pus and relieve pressure.
- Surgical Removal: In cases of recurring or large infected cysts, surgical removal may be necessary. The entire cyst is excised under local anesthesia to prevent it from reoccurring. After the procedure, proper wound care is essential to prevent further infections.
Conclusion
Infected sebaceous cysts are common but can be easily treated with the right approach. If you notice any signs of infection, such as pain, redness, or pus drainage, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider. Prompt treatment can prevent complications and ensure effective management of the cyst. In some cases, surgical removal may be the most effective long-term solution. Always seek professional medical advice for the best care and treatment options.