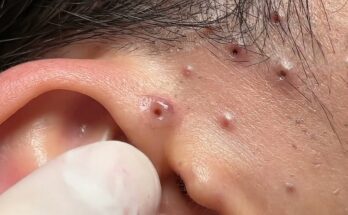
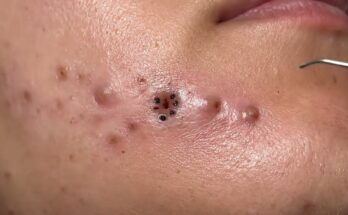
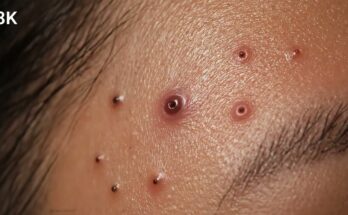
Acne is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages, from teenagers to adults. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and sometimes bacteria. The result is pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and cysts. Although acne is most common during adolescence, it can persist into adulthood, leading many to seek effective treatments. Fortunately, several treatments can help manage acne, ranging from over-the-counter remedies to professional interventions.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments
For mild to moderate acne, many people begin with OTC products. These treatments typically contain ingredients such as benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, sulfur, or alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs). Benzoyl peroxide is a powerful ingredient that kills acne-causing bacteria and helps to unclog pores, while salicylic acid works by exfoliating the skin and clearing dead cells that may block pores. Sulfur, though less common, helps reduce oil production and has antimicrobial properties. AHAs, including glycolic acid, help to exfoliate the skin and prevent clogged pores.
Many OTC acne treatments are available in various forms, such as creams, gels, cleansers, and spot treatments, allowing people to find an option that works best for their skin type. However, it’s important to note that these treatments can take time to show results, often requiring several weeks of consistent use.
Topical Prescription Treatments
For more persistent acne, a healthcare provider may recommend prescription-strength topical treatments. These include stronger forms of benzoyl peroxide or retinoids. Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, help to speed up skin cell turnover, preventing clogged pores and reducing inflammation. Common retinoids include tretinoin and adapalene. While effective, retinoids can cause skin dryness and irritation, so they are usually introduced gradually.
Oral Medications
For severe cases of acne, oral medications may be prescribed. Antibiotics, such as doxycycline or minocycline, can reduce inflammation and kill bacteria. Oral contraceptives may also help, particularly for women, as they regulate hormones that can trigger acne. In some cases, a more potent medication known as isotretinoin (Accutane) may be prescribed for cystic acne. While isotretinoin is highly effective, it can have serious side effects, so it is typically considered a last resort.
Professional Treatments
In-office treatments can also help with more stubborn acne. Chemical peels use strong acids to exfoliate the skin, while laser treatments target acne-causing bacteria and reduce oil production. Additionally, light therapy can help kill bacteria and reduce inflammation. These treatments often require multiple sessions and may be used in conjunction with other forms of acne management.
Conclusion
Acne treatment varies depending on the severity and type of acne, but there are many effective options available. From OTC solutions to professional treatments, it’s essential to find a regimen that suits your skin and lifestyle. Consulting with a dermatologist can help determine the best course of action, ensuring that you get the clear, healthy skin you deserve.